Allergies are a common health problem affecting millions of people worldwide. They occur when the immune system reacts to normally harmless substances, such as pollen, dust, or certain foods. A wide range of allergens can trigger allergies, and their symptoms can range from mild to severe, sometimes even life-threatening.
The pathophysiology of allergies involves an abnormal immune response to an otherwise harmless substance known as an allergen. In a normal immune response, the immune system recognizes and attacks foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses, to protect the body. However, the immune system mistakenly identifies an allergen as a threat in people with allergies and overreacts to it.
The immune system’s response to an allergen involves activating various immune cells, including mast cells and eosinophils. When the immune system encounters an allergen, it produces an antibody called immunoglobulin E (IgE), which binds to mast cells and triggers the release of inflammatory mediators, such as histamine and leukotrienes.
The release of these inflammatory mediators leads to the symptoms of allergies, such as sneezing, itching, hives, swelling, and mucus production. In more severe cases, the immune response can trigger life-threatening anaphylaxis, which can cause difficulty breathing, low blood pressure, and shock.

The specific allergen that triggers an immune response varies depending on the individual. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, animal dander, certain foods, and insect venom.
Allergies can be managed through various approaches, including avoiding allergens, medication, and immunotherapy. Treatment options depend on the severity of the allergy and the individual’s specific needs.
In this blog, we will explore 6 tips for managing common allergens.
1. Know your allergens
The first step in managing allergies is identifying the allergen that triggers your symptoms. Some of the most common allergens include pollen, dust mites, animal dander, mold, and certain foods. You can work with an allergist to identify your allergens through skin or blood tests.
Once you know your allergens, you can minimize your exposure to them. For example, if you are allergic to pollen, you can avoid going outside during peak pollen season or wear a mask to reduce exposure.
There are medical procedures that can help identify your allergies. These procedures are typically done by an allergist, a doctor specializing in diagnosing and treating allergies. Looking for an allergy doctor near me will help you filter out the best allergist in your area.
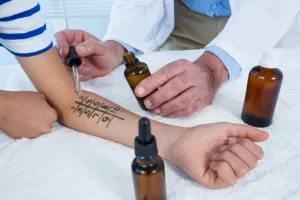
One common procedure is a skin prick test, which involves placing a small amount of allergen on your skin and then pricking the skin to allow the allergen to enter the body. If you are allergic to the allergen, you will develop a small bump or redness at the site of the prick.
Another procedure is a blood test, which measures the number of antibodies your body produces in response to specific allergens. The blood test results can help your doctor identify the allergen that is triggering your symptoms.
Sometimes, your doctor may also recommend a food challenge test, which involves gradually introducing small amounts of a food allergen to your diet to see if you react.
It is important to note that these procedures should only be done under the supervision of a healthcare provider, as they can be potentially dangerous if not done correctly. If you suspect you have allergies, seeking medical attention and getting a proper diagnosis is important.
2. Keep your environment clean
Dust mites, mold, and animal dander are common indoor allergens. To reduce exposure to these allergens, it is important to keep your environment clean. Vacuum your carpets and furniture regularly, use a dehumidifier to control moisture levels in your home, and wash your bedding in hot water once a week.
If you have a pet, it is important to bathe them regularly and keep them out of your bedroom. You can also use air purifiers to filter out allergens from the air.
Here are some tips for keeping your home clean and free of allergens:
- Vacuum regularly: Vacuum your carpets, rugs, and furniture at least once a week using a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter. This will help to remove dust mites and other allergens that can accumulate in your home.
- Wash bedding frequently: Wash your sheets, pillowcases, and blankets in hot water at least once a week. This will help to kill dust mites and remove any allergens that may have accumulated on your bedding.
- Use allergen-proof covers: Use allergen-proof covers for your mattress, pillows, and box spring. These covers can help to prevent dust mites and other allergens from accumulating in your bedding.
- Control humidity: Use a dehumidifier to control humidity levels in your home, especially in areas prone to moisture buildups, such as the bathroom and basement. This will help to prevent mold growth and reduce the risk of mold-related allergies.
- Clean air ducts and filters: Have your air ducts and filters cleaned regularly to prevent dust accumulation and other allergens in your home’s ventilation system.
- Keep pets out of the bedroom: If you have pets, keep them out to reduce exposure to animal dander. Use a HEPA filter air purifier in the rooms where your pets spend the most time.
Following these tips can create a cleaner, healthier environment less likely to trigger your allergies.
3. Avoid certain foods
Food allergies are becoming increasingly common and can be severe in some cases. If you have a food allergy, it is important to avoid the allergen completely. Common food allergens include peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, eggs, milk, and soy.
Be sure to read food labels carefully and ask about ingredients when eating out. You may also want to carry an epinephrine auto-injector (such as an EpiPen) in case of a severe reaction.

An EpiPen is a type of epinephrine auto-injector that can be used to treat severe allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis. Here are the general steps for using an EpiPen:
- Remove the EpiPen from its protective case. Ensure that the expiration date has not passed and the liquid inside is clear and not discolored.
- Hold the EpiPen firmly with the orange tip pointing downward. Do not touch the black tip at the other end, as this is where the needle is located.
- Pull off the blue safety cap. This will expose the black tip.
- Hold the EpiPen with your fist around the middle of the device. Please do not hold it with your fingers near the black tip, as this can accidentally trigger the device.
- Place the black tip against the middle of the outer thigh. Press the tip firmly into the thigh until you hear a click. This will release the needle and deliver the epinephrine.
- Hold the EpiPen for several seconds to ensure all the medication has been delivered.
- Remove the EpiPen from your thigh and massage the injection site for 10 seconds to help the epinephrine be absorbed.
- Seek emergency medical attention immediately, even if your symptoms improve. Anaphylaxis can be life-threatening and requires prompt medical attention.
Remember to always carry your EpiPen with you if you have a known severe allergy, and ensure your friends and family know how to use it in an emergency. Replacing your EpiPen before the expiration date is also important to ensure it is still effective.
4. Take medication
Many medications are available to treat allergies, including antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal sprays. These medications can help alleviate sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes.
Working with a healthcare provider is important to determine which medication is best for you and how to use it safely. Some medications can cause side effects, and others may interact with your other medications.
Anti-allergy drugs work by targeting different components of the immune response that causes allergic reactions. Here are some of the main classes of anti-allergy drugs and their pharmacology:
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the immune system that causes many of the symptoms of allergies, such as sneezing, itching, and a runny nose. Antihistamines can be either first-generation (such as diphenhydramine) or second-generation (such as loratadine). Second-generation antihistamines are preferred because they are less sedating than first-generation drugs.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory drugs that suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation. They are often used to treat severe allergies or asthma. Corticosteroids can be inhaled (such as fluticasone) or taken orally (such as prednisone). These medications are commonly seen in an allergy and asthma center.
- Leukotriene modifiers: Leukotriene modifiers work by blocking the action of leukotrienes, chemicals released by the immune system that cause inflammation and constriction of the airways. Leukotriene modifiers (such as montelukast) can be taken orally and are often used to treat asthma.
- Mast cell stabilizers: Mast cell stabilizers prevent the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators from mast cells, a type of immune cell involved in allergic reactions. Mast cell stabilizers can be inhaled (such as cromolyn) or taken orally (such as ketotifen).
- Immunomodulators: Immunomodulators target the immune system and reduce the severity of allergic reactions. One example is omalizumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds to IgE, an antibody involved in allergic reactions, and prevents it from triggering an immune response.
- Decongestants: Decongestants narrow blood vessels in the nasal passages, reducing swelling and congestion. They can be taken orally (such as pseudoephedrine) or applied topically (such as oxymetazoline). Decongestants can cause side effects such as increased heart rate and blood pressure and should be used cautiously in people with certain medical conditions.
The choice of anti-allergy drug depends on the type and severity of the allergy, the individual’s medical history, and other factors. Working with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs is important.
5. Practice good hygiene
Good hygiene is important for managing allergies, especially if you have hay fever or other seasonal allergies. Pollen can stick to your skin and hair, so it is important to shower and wash your hair after spending time outdoors during the peak pollen season.
Wash your hands frequently to prevent the spread of germs and allergens. Avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth, as this can introduce allergens into your body.
6. Consider immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, is a treatment that involves regular injections of small amounts of an allergen to desensitize the immune system. Over time, this can help reduce the severity of allergy symptoms.
Immunotherapy is typically reserved for people with severe allergies or who do not respond to other treatments. It can take several months or even years to see a significant improvement, and the treatment can be costly and time-consuming.
Conclusion
Managing allergies can be challenging, but the right approach can reduce your symptoms and improve your quality of life. By identifying your allergens, keeping your environment clean, avoiding certain foods, taking medication, practicing good hygiene, and considering immunotherapy, you can take control of your allergies and minimize their impact on your daily life. Working with a healthcare provider or allergist is important to develop a personalized allergy management plan that meets your needs.
Remember that allergies can be unpredictable, and even with the best management plan, you may experience symptoms occasionally. Be patient, stay informed, and don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if your symptoms worsen or you have a severe reaction.
With these tips and a proactive approach, you can manage your allergies and live healthier, more comfortable lives.
Agape Family Health is dedicated to eliminating health inequalities and ensuring everyone can access high-quality medical care in Jacksonville, Florida. Agape Family Health is working to lessen health inequities and enhance the health and well-being of all residents in the Jacksonville area by adopting a holistic and cooperative approach. Stay in touch with us!



